Department of General Relativity and Astronomy, Kazan State University, Lenin street 18, Kazan, 420008, Russia
In recent years, bifurcation theory has undergone a tremendous development with an infusion of new ideas and methods from dynamical systems and catastrophes of Arnold-Thom theory. As a result, it is difficult to draw the boundaries of the theory with ant confidence. These theories are very important for investigation of resonance motion in celestial mechanics.
The synchronization in dynamical systems can been considered as consequence of the strong manifestation of stable, regulated behaviour of phase trajectory. Because, the dynamical systems should be take a equilibrium states as type a attractive node or focus.
The capture of the Moon represents a very unique event in the history of the solar system. The gravitational angular momentum can itself provided stable resonance rotation, which is described by generalized Cassini lows. However, the initial data of motion can lie out of a resonance zone. So, a mechanism, which is provide sufficiently high probability capture at resonance zone should be proposed. The tidal friction theory is very interesting model for this case.
In this report for the plane motion we are analyzing the differential equations systems of gravitational capture of the early Moon at the resonance rotation with action of gravitational torque by qualitative analysis and bifurcation theory of dynamical systems at General Relativity and Gravitation.
The successive analysis of the phase portraits of one, two, three- parameter dynamical systems and of the bifurcation space of parameters {a,b, c} confirms of gravitational capture - tightening of phase trajectory to the resonance zone and attracting center (node and focus). There are a simple equilibrium state by the saddle, node, focus, center types and/or complicated equilibrium states - saddle-node and degenerate saddle-node.
At the phase space for any parameters are creating or annihilating rough and non-rough dynamical systems of first and second degrees roughness. The conditions
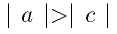
is necessity conditions for existence equilibrium state, connecting to resonance rotations of the Moon. The additional condition b<0 is also necessary for gravitational capture at resonance rotation of the Moon. The analyzed DS bifurcations fill total spectrum of the phase portraits reconstruction of gravitational capture, which is typical for the non-rough first and second degrees non-roughness.
At the phase space for any parameters rough and non-rough dynamical systems of first and second degrees roughness arise or disappear.
The separation of 3-dimensional parameter space of dynamical system by bifurcation surfaces is obtained. The gallery of more than seventeen phase portraits of gravitational capture extends the known scenario of cosmogonical evolution of the Moon on the early time.